Prevention of Osteoarthritis
1. Regular exercise
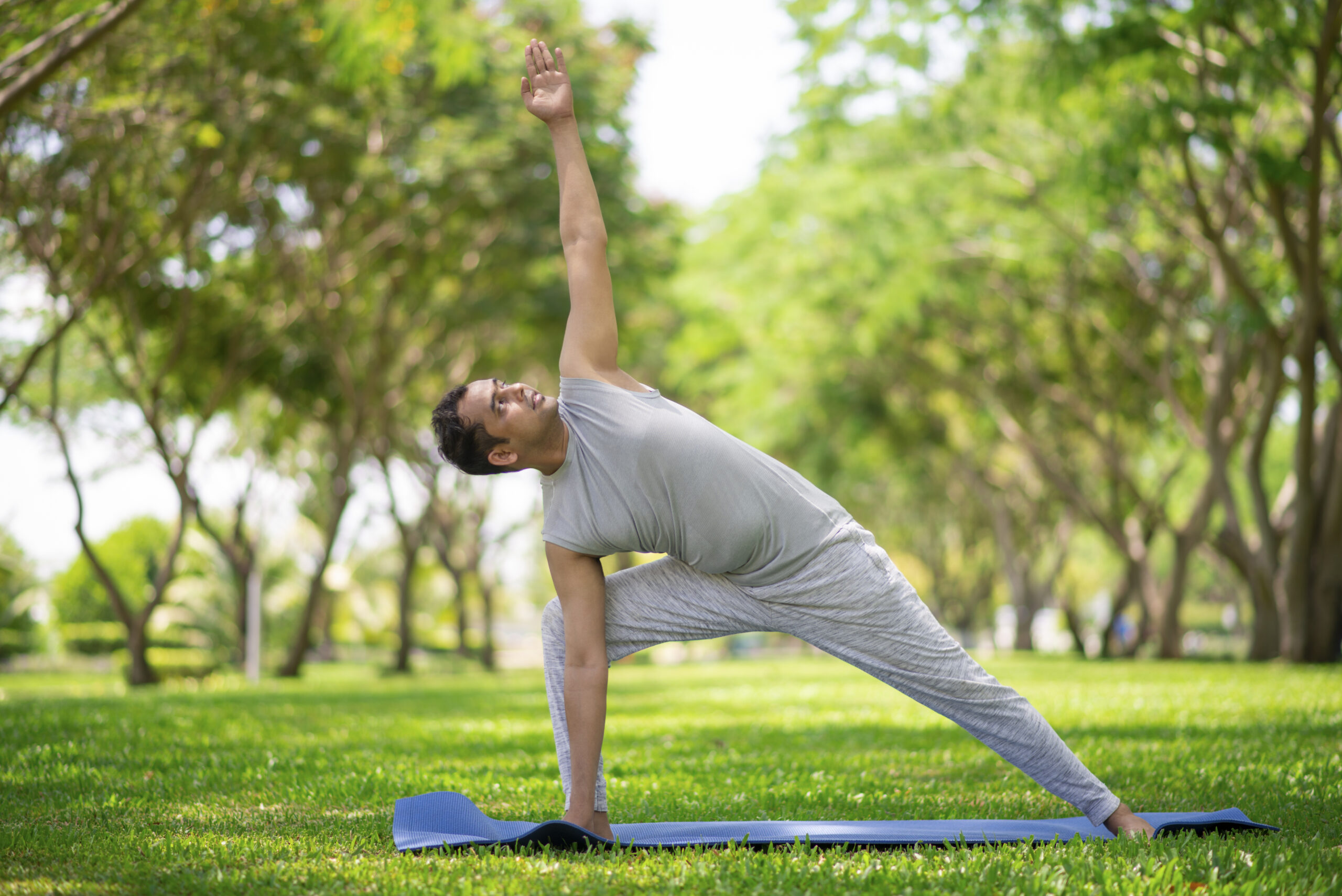

Regular exercise is an important component of managing osteoarthritis and improving joint health. Exercise can help reduce pain, improve joint mobility and flexibility, increase muscle strength, and improve overall physical function.
Types of exercises that are beneficial for people with osteoarthritis include:
- Aerobic exercise: Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can help improve cardiovascular health, reduce pain and stiffness, and improve joint function.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises, such as weight lifting, can help build muscle strength and improve joint stability.
- Stretching exercises: Stretching exercises, such as yoga, can help improve flexibility and range of motion.
- Low-impact exercises: Low-impact exercises, such as water aerobics, can be beneficial for people with osteoarthritis who have joint pain or stiffness and may not be able to participate in high-impact activities.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist before starting an exercise program. They can help design a safe and effective exercise program that takes into account your specific needs and limitations. Regular exercise can be a valuable tool in managing osteoarthritis and improving overall health and quality of life.
2. Maintaining a healthy weight

Maintaining a healthy weight is an important factor for managing osteoarthritis and reducing the strain on joints. Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis and worsen existing joint problems.
Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the hips, knees, and ankles, which can lead to joint damage and increase pain and stiffness. By maintaining a healthy weight, people with osteoarthritis can reduce the strain on their joints and improve their overall joint health.
There are several strategies for maintaining a healthy weight, including:
- Eating a healthy diet: A balanced diet that is low in processed foods and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help control weight and improve overall health.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Regular physical activity can help burn calories, improve cardiovascular health, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Monitoring portion sizes: Paying attention to portion sizes can help prevent overeating and reduce calorie intake.
- Seeking support from a healthcare provider or dietitian: A healthcare provider or dietitian can provide guidance and support on healthy weight management strategies.
Maintaining a healthy weight is an important step in managing osteoarthritis and improving overall joint health. By following a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, people with osteoarthritis can reduce the strain on their joints and improve their quality of life.
3. Avoiding joint injury
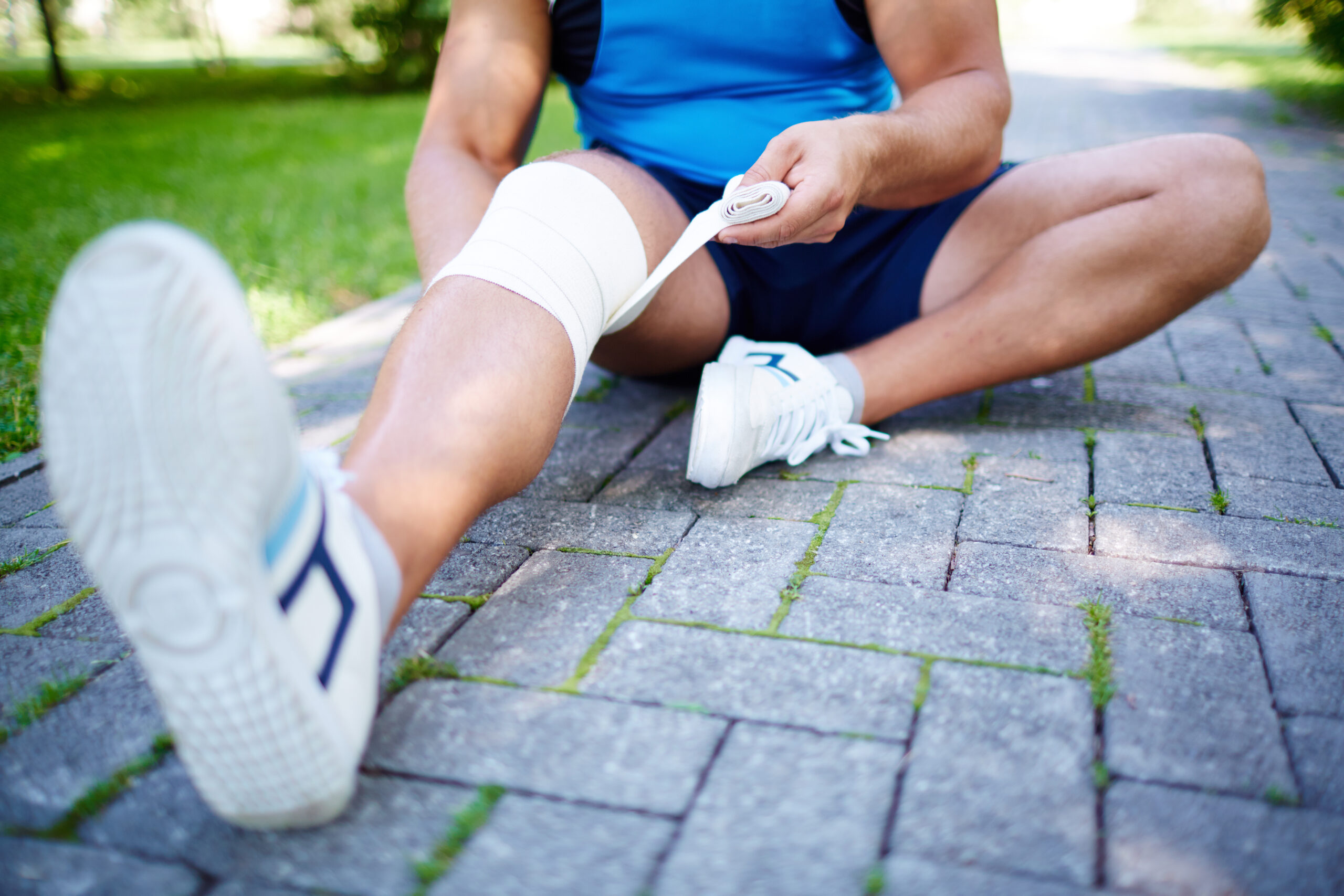

Avoiding joint injury is important in preventing and managing osteoarthritis. Joint injuries can cause lasting damage to the joint and increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Here are some tips for avoiding joint injury:
- Use proper technique when performing physical activities: Using proper technique when performing physical activities, such as lifting heavy objects or playing sports, can help reduce the risk of joint injury.
- Wear proper protective gear: Wearing proper protective gear, such as knee pads or wrist guards, can help reduce the risk of joint injury during high-impact activities.
- Avoid repetitive motions: Repetitive motions, such as typing or playing musical instruments, can cause joint strain and increase the risk of injury. Taking breaks and practicing proper posture can help reduce the risk of injury.
- Manage arthritis-related pain: Managing arthritis-related pain can help reduce the risk of joint injury by reducing the need to compensate for pain.
- Strengthen the muscles around the joint: Strengthening the muscles around the joint can help reduce the risk of injury and improve joint stability.
By following these tips, people with osteoarthritis can reduce their risk of joint injury and improve the health of their joints. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding joint injury are all important steps in managing osteoarthritis and improving overall joint health.
4. Proper posture and body mechanics
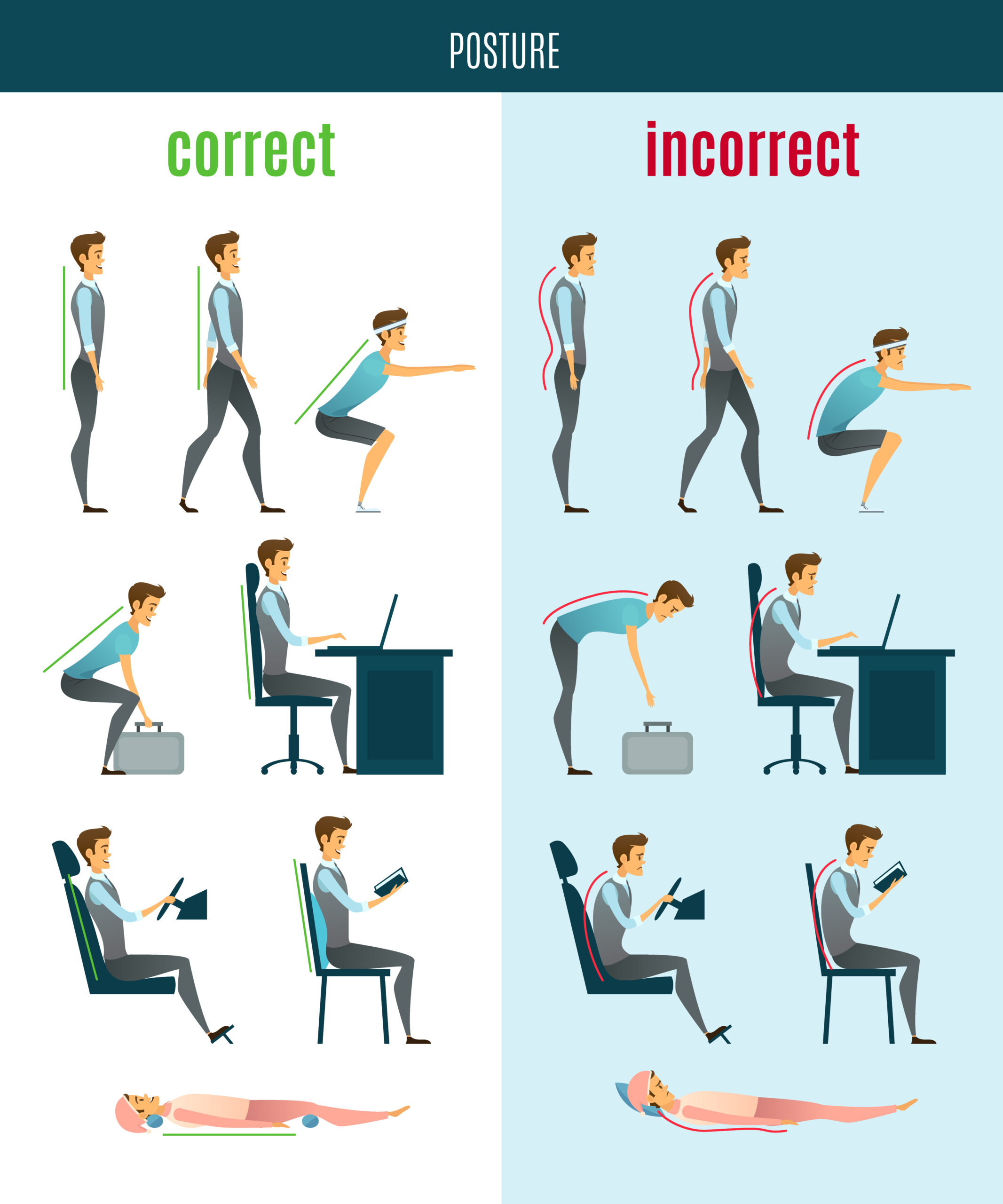
Proper posture and body mechanics play a key role in reducing the risk of joint injury and managing osteoarthritis. Here’s why:
- Reduced stress on joints: Good posture reduces the stress placed on joints, which helps to minimize joint damage and reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Improved balance and stability: Good posture helps improve balance and stability, which can help reduce the risk of falls and joint injury.
- Reduced pain: Good posture can help reduce pain by reducing the strain placed on joints and muscles.
- Increased mobility: Good posture can help improve joint mobility and flexibility, which can help improve the range of motion and reduce the risk of joint injury.
To maintain good posture, it’s important to:
- Stand up straight: Keep your shoulders back, chest up, and abdomen in.
- Use proper body mechanics when lifting heavy objects: Keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back.
- Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing: Take breaks and stretch regularly to prevent stiff joints and muscles.
- Sleep in a supportive position: Use a supportive mattress and pillows to maintain good posture while sleeping.
By maintaining good posture and using proper body mechanics, people with osteoarthritis can reduce the risk of joint injury and manage their symptoms more effectively.
Relevant Resource : Hairline Fracture

