What is Osteoarthritis?
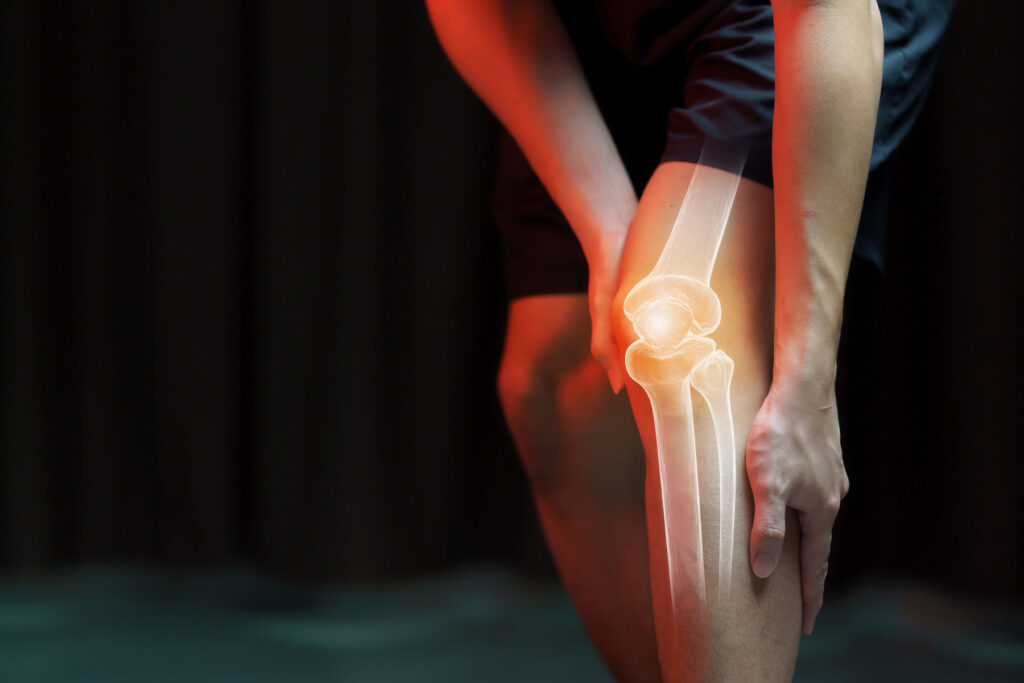
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the joints and is characterized by the gradual degradation and eventual loss of cartilage. Cartilage is a smooth, flexible tissue that covers the ends of bones and acts as a cushion, allowing for smooth and painless joint movement. Over time, the cartilage in the joint can wear down and become thin, leading to bone-on-bone contact. This can cause pain, swelling, and a limited range of motion in the affected joint.
Osteoarthritis is often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis because it’s caused by the normal aging process and the daily wear and tear on joints. However, it can also be caused by other factors such as obesity, joint injury, and genetics. The condition is most commonly found in the hands, knees, and hips typically affecting people over 50.
It’s important to note that osteoarthritis is different from other types of arthritis, -such as rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that results from the gradual loss of cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is caused by an immune system attack on the joints.
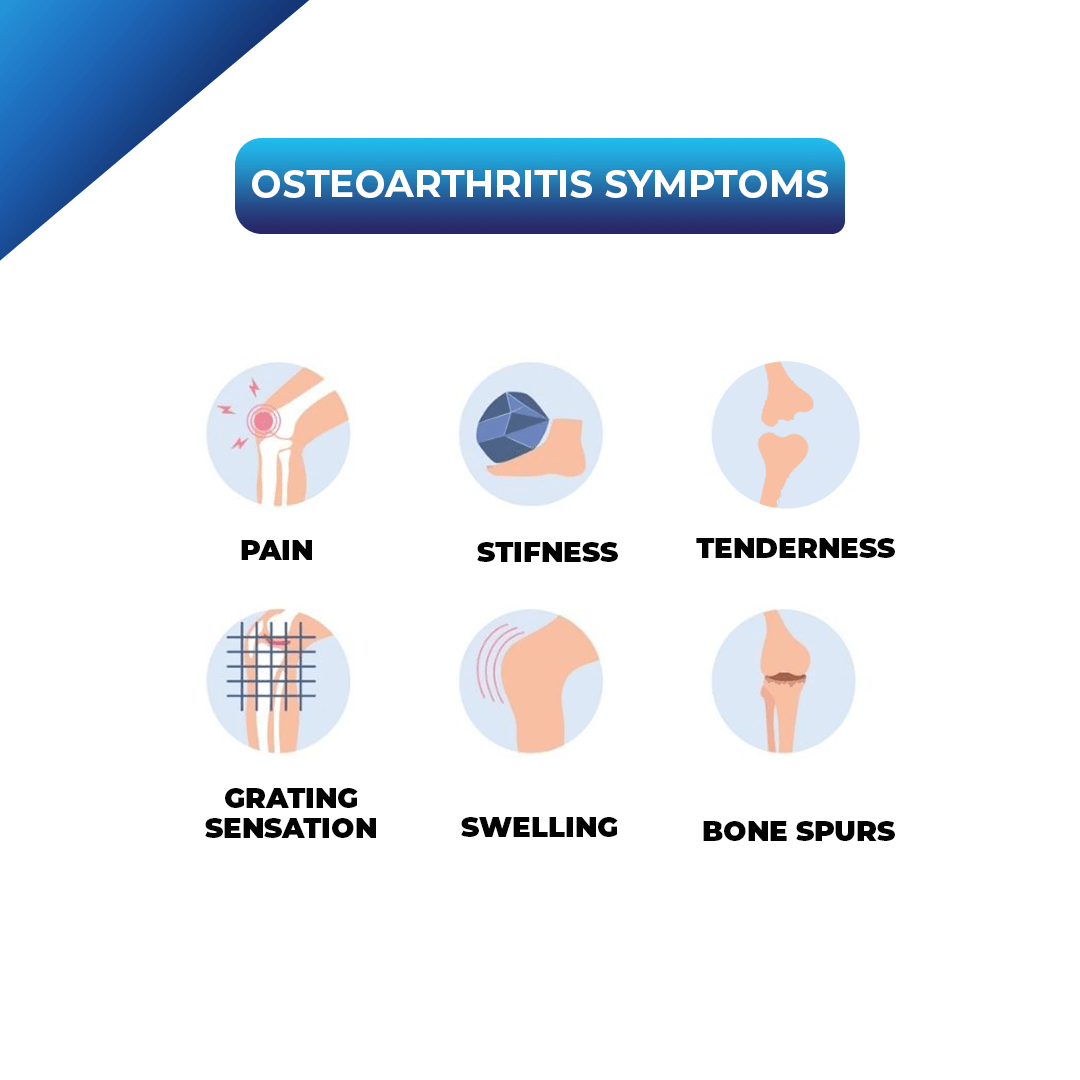
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis:
- Pain: The most common symptom of osteoarthritis is pain in the affected joint, which can range from a dull ache to a sharp, shooting pain.
- Swelling: Osteoarthritis can cause swelling in the affected joint, which can be painful and limit the range of motion.
- Stiffness: The joint may feel stiff, particularly after periods of inactivity, such as sitting or lying down
- Limited range of motion: The joint may feel tight and have limited mobility, making it difficult to perform everyday activities.
- Crackling sound when moving the joint: People with osteoarthritis may hear a crackling or popping sound when they move the affected joint.
- Decreased ability to perform daily activities: Osteoarthritis can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks, such as walking, climbing stairs, or lifting objects.
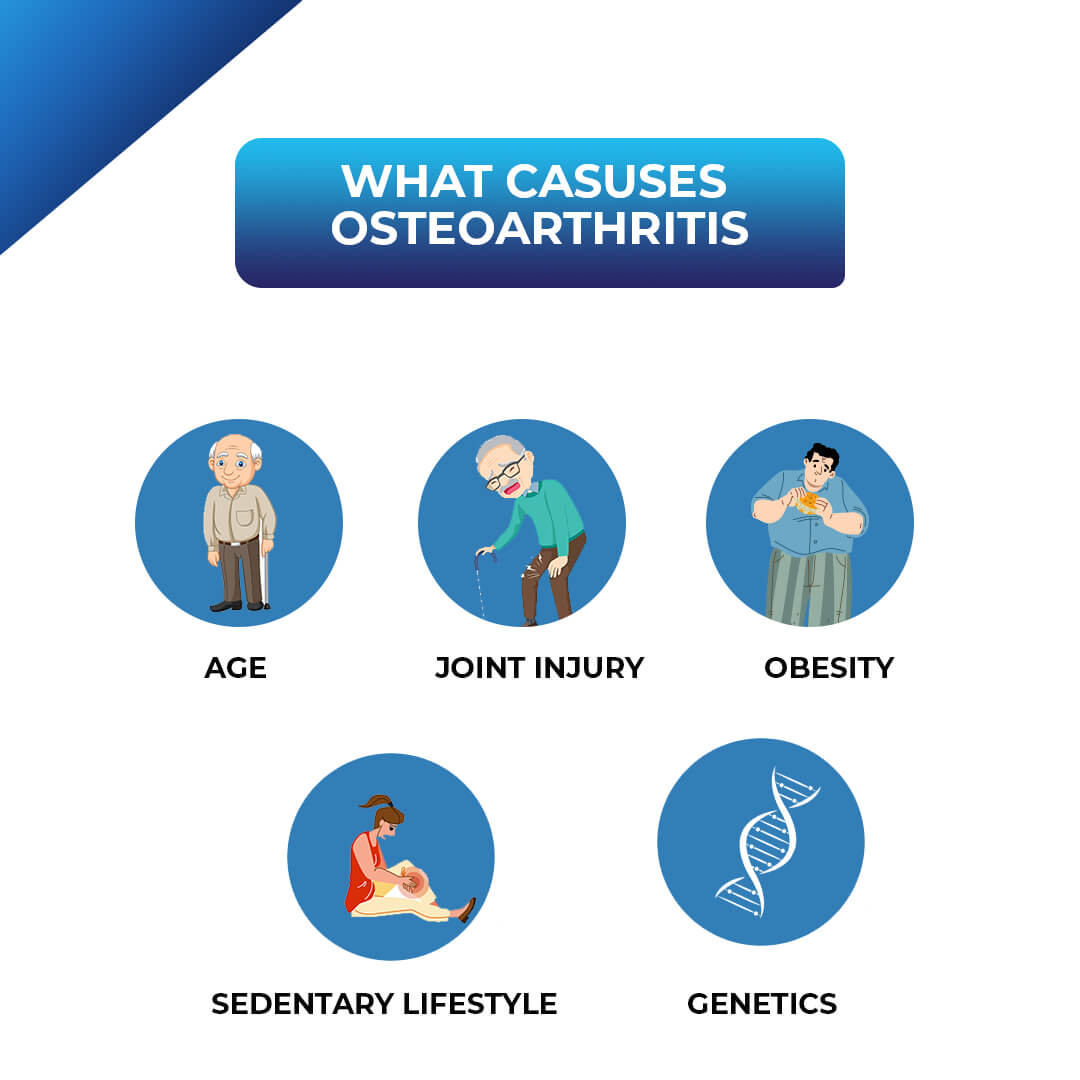
Causes of Osteoarthritis:
- Age: As people get older, the joints naturally wear down and lose their
cartilage, making them more susceptible to osteoarthritis. - Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop osteoarthritis due to
genetic factors that make their joints more vulnerable to damage. - Joint injury: Previous injury to a joint, such as a fracture or a ligament
tear, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis later in life. - Obesity: Excessive weight puts additional stress on joints, particularly
the knees, hips, and lower back, which can lead to the development of
osteoarthritis. - Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can lead to weak muscles
and joints, which can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Importance of early diagnosis and treatment of Osteoarthritis
Early diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis are important for several reasons:
- Slows the progression of the disease: Osteoarthritis is a progressive disease, meaning it will continue to worsen over time if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment can help slow the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of joint damage.
- Relieves pain: Early treatment can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the affected joint, improving quality of life.
- Maintains joint mobility: Early treatment can help maintain joint mobility and flexibility, reducing the risk of joint stiffness and improving the ability to perform everyday activities
- Avoids surgery: In severe cases of osteoarthritis, surgery may be required to replace the affected joint. Early diagnosis and treatment can help avoid the need for surgery by slowing the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of joint damage.
- Improves overall health: Osteoarthritis can significantly impact overall health, including physical and emotional well-being. Early diagnosis and treatment can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with the disease.
It’s important for people to be aware of the symptoms of osteoarthritis and to seek medical attention if they experience pain or discomfort in their joints. An early diagnosis can help ensure that appropriate treatment is started, reducing the risk of joint damage and improving the chances of successful management of the disease.
Relevant Resource : Hairline Fracture

